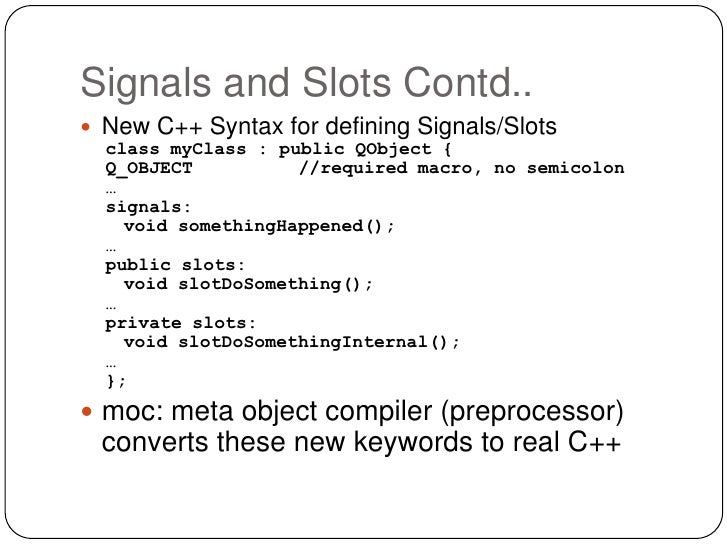
Qt Signals Slots Threads
Dear Qt Forum, currently I am developing a hobby project with Qt and wanted to use signals and slots across threads (without QThread inheritance). Sorry for bringing up this topic again, but I am a bit stuck to create signals and slots across threads with. Direct connection means that emitting the signal and calling the slot are shortcutted to a simple method call, making the emit call jump directly into the slot.Queued connection puts the call into a queue, which is handled as soon as the Qt event loop is running again, or you force it by calling QCoreApplication::processEvents, in line with all other events that have been queued until then.
Example
Some times you see a signal is emitted in sender thread but connected slot doesn't called (in other words it doesn't receive signal), you have asked about it and finaly got that the connection type Qt::DirectConnection would fix it, so the problem found and everything is ok.
But generaly this is bad idea to use Qt:DirectConnection until you really know what is this and there is no other way. Lets explain it more, Each thread created by Qt (including main thread and new threads created by QThread) have Event loop, the event loop is responsible for receiving signals and call aproporiate slots in its thread. Generaly executing a blocking operation inside an slot is bad practice, because it blocks the event loop of that threads so no other slots would be called.
If you block an event loop (by making very time consuming or blocking operation) you will not receive events on that thread until the event loop will be unblocked. If the blocking operation, blocks the event loop forever (such as busy while), the slots could never be called.
In this situation you may set the connection type in connect to Qt::DirectConnection, now the slots will be called even the event loop is blocked. so how this could make broke everything? In Qt::DirectConnection Slots will be called in emiter threads, and not receiver threads and it can broke data synchronizations and ran into other problems. So never use Qt::DirectConnection unless you know what are you doing. If your problem will be solved by using Qt::DirectConnection, you have to carefull and look at your code and finding out why your event loop is blocked. Its not a good idea to block the event loop and its not recomended in Qt.
Here is small example which shows the problem, as you can see the nonBlockingSlot would be called even the blockingSlot blocked event loop with while(1) which indicates bad coding
The QThread class provides a platform-independent way to manage threads. More...
| Header: | #include <QThread> |
| qmake: | QT += core |
| Inherits: | QObject |
Public Types
| enum | Priority { IdlePriority, LowestPriority, LowPriority, NormalPriority, ..., InheritPriority } |
Public Functions
| QThread(QObject *parent = Q_NULLPTR) | |
| ~QThread() | |
| QAbstractEventDispatcher * | eventDispatcher() const |
| void | exit(int returnCode = 0) |
| bool | isFinished() const |
| bool | isInterruptionRequested() const |
| bool | isRunning() const |
| int | loopLevel() const |
| Priority | priority() const |
| void | requestInterruption() |
| void | setEventDispatcher(QAbstractEventDispatcher *eventDispatcher) |
| void | setPriority(Priority priority) |
| void | setStackSize(uint stackSize) |
| uint | stackSize() const |
| bool | wait(unsigned long time = ULONG_MAX) |
Reimplemented Public Functions
- 32 public functions inherited from QObject
Public Slots
| void | quit() |
| void | start(Priority priority = InheritPriority) |
| void | terminate() |
- 1 public slot inherited from QObject
Signals
- 2 signals inherited from QObject
Static Public Members
| QThread * | currentThread() |
| Qt::HANDLE | currentThreadId() |
| int | idealThreadCount() |
| void | msleep(unsigned long msecs) |
| void | sleep(unsigned long secs) |
| void | usleep(unsigned long usecs) |
| void | yieldCurrentThread() |
- 11 static public members inherited from QObject
Protected Functions
- 9 protected functions inherited from QObject
Static Protected Members
| void | setTerminationEnabled(bool enabled = true) |
Additional Inherited Members
- 1 property inherited from QObject
Detailed Description
The QThread class provides a platform-independent way to manage threads.
A QThread object manages one thread of control within the program. QThreads begin executing in run(). By default, run() starts the event loop by calling exec() and runs a Qt event loop inside the thread.
You can use worker objects by moving them to the thread using QObject::moveToThread().
The code inside the Worker's slot would then execute in a separate thread. However, you are free to connect the Worker's slots to any signal, from any object, in any thread. It is safe to connect signals and slots across different threads, thanks to a mechanism called queued connections.
Another way to make code run in a separate thread, is to subclass QThread and reimplement run(). For example:
In that example, the thread will exit after the run function has returned. There will not be any event loop running in the thread unless you call exec().
It is important to remember that a QThread instance lives in the old thread that instantiated it, not in the new thread that calls run(). This means that all of QThread's queued slots will execute in the old thread. Thus, a developer who wishes to invoke slots in the new thread must use the worker-object approach; new slots should not be implemented directly into a subclassed QThread.
When subclassing QThread, keep in mind that the constructor executes in the old thread while run() executes in the new thread. If a member variable is accessed from both functions, then the variable is accessed from two different threads. Check that it is safe to do so.
Qt Signals Slots Threads Double Diamond
Note: Care must be taken when interacting with objects across different threads. See Synchronizing Threads for details.
Managing Threads
QThread will notifiy you via a signal when the thread is started() and finished(), or you can use isFinished() and isRunning() to query the state of the thread.
You can stop the thread by calling exit() or quit(). In extreme cases, you may want to forcibly terminate() an executing thread. However, doing so is dangerous and discouraged. Please read the documentation for terminate() and setTerminationEnabled() for detailed information.
From Qt 4.8 onwards, it is possible to deallocate objects that live in a thread that has just ended, by connecting the finished() signal to QObject::deleteLater().
Use wait() to block the calling thread, until the other thread has finished execution (or until a specified time has passed).
QThread also provides static, platform independent sleep functions: sleep(), msleep(), and usleep() allow full second, millisecond, and microsecond resolution respectively. These functions were made public in Qt 5.0.
Note: wait() and the sleep() functions should be unnecessary in general, since Qt is an event-driven framework. Instead of wait(), consider listening for the finished() signal. Instead of the sleep() functions, consider using QTimer.
The static functions currentThreadId() and currentThread() return identifiers for the currently executing thread. The former returns a platform specific ID for the thread; the latter returns a QThread pointer.
To choose the name that your thread will be given (as identified by the command ps -L on Linux, for example), you can call setObjectName() before starting the thread. If you don't call setObjectName(), the name given to your thread will be the class name of the runtime type of your thread object (for example, 'RenderThread' in the case of the Mandelbrot Example, as that is the name of the QThread subclass). Note that this is currently not available with release builds on Windows.

See also Thread Support in Qt, QThreadStorage, Synchronizing Threads, Mandelbrot Example, Semaphores Example, and Wait Conditions Example.
Member Type Documentation
enum QThread::Priority
This enum type indicates how the operating system should schedule newly created threads.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QThread::IdlePriority | 0 | scheduled only when no other threads are running. |
QThread::LowestPriority | 1 | scheduled less often than LowPriority. |
QThread::LowPriority | 2 | scheduled less often than NormalPriority. |
QThread::NormalPriority | 3 | the default priority of the operating system. |
QThread::HighPriority | 4 | scheduled more often than NormalPriority. |
QThread::HighestPriority | 5 | scheduled more often than HighPriority. |
QThread::TimeCriticalPriority | 6 | scheduled as often as possible. |
QThread::InheritPriority | 7 | use the same priority as the creating thread. This is the default. |
Member Function Documentation
QThread::QThread(QObject *parent = Q_NULLPTR)
Constructs a new QThread to manage a new thread. The parent takes ownership of the QThread. The thread does not begin executing until start() is called.
See also start().
QThread::~QThread()
Destroys the QThread.
Note that deleting a QThread object will not stop the execution of the thread it manages. Deleting a running QThread (i.e. isFinished() returns false) will result in a program crash. Wait for the finished() signal before deleting the QThread.
[static] QThread *QThread::currentThread()
Returns a pointer to a QThread which manages the currently executing thread.
[static] Qt::HANDLE QThread::currentThreadId()
Returns the thread handle of the currently executing thread.
Warning: The handle returned by this function is used for internal purposes and should not be used in any application code.
Warning: On Windows, the returned value is a pseudo-handle for the current thread. It can't be used for numerical comparison. i.e., this function returns the DWORD (Windows-Thread ID) returned by the Win32 function getCurrentThreadId(), not the HANDLE (Windows-Thread HANDLE) returned by the Win32 function getCurrentThread().
[virtual] bool QThread::event(QEvent *event)
Reimplemented from QObject::event().
QAbstractEventDispatcher *QThread::eventDispatcher() const
Returns a pointer to the event dispatcher object for the thread. If no event dispatcher exists for the thread, this function returns 0.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.0.
See also setEventDispatcher().
[protected] int QThread::exec()
Enters the event loop and waits until exit() is called, returning the value that was passed to exit(). The value returned is 0 if exit() is called via quit().
This function is meant to be called from within run(). It is necessary to call this function to start event handling.
See also quit() and exit().
void QThread::exit(intreturnCode = 0)
Tells the thread's event loop to exit with a return code.
After calling this function, the thread leaves the event loop and returns from the call to QEventLoop::exec(). The QEventLoop::exec() function returns returnCode.
By convention, a returnCode of 0 means success, any non-zero value indicates an error.
Note that unlike the C library function of the same name, this function does return to the caller -- it is event processing that stops.
No QEventLoops will be started anymore in this thread until QThread::exec() has been called again. If the eventloop in QThread::exec() is not running then the next call to QThread::exec() will also return immediately.
See also quit() and QEventLoop.
[signal] void QThread::finished()
This signal is emitted from the associated thread right before it finishes executing.
When this signal is emitted, the event loop has already stopped running. No more events will be processed in the thread, except for deferred deletion events. This signal can be connected to QObject::deleteLater(), to free objects in that thread.
Note: If the associated thread was terminated using terminate(), it is undefined from which thread this signal is emitted.
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
See also started().
[static] int QThread::idealThreadCount()
Returns the ideal number of threads that can be run on the system. This is done querying the number of processor cores, both real and logical, in the system. This function returns -1 if the number of processor cores could not be detected.
bool QThread::isFinished() const
Returns true if the thread is finished; otherwise returns false.
See also isRunning().
bool QThread::isInterruptionRequested() const
Return true if the task running on this thread should be stopped. An interruption can be requested by requestInterruption().
This function can be used to make long running tasks cleanly interruptible. Never checking or acting on the value returned by this function is safe, however it is advisable do so regularly in long running functions. Take care not to call it too often, to keep the overhead low.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.2.
See also currentThread() and requestInterruption().
bool QThread::isRunning() const
Returns true if the thread is running; otherwise returns false.
See also isFinished().
int QThread::loopLevel() const
Returns the current event loop level for the thread.
Note: This can only be called within the thread itself, i.e. when it is the current thread.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.5.
[static] void QThread::msleep(unsignedlongmsecs)
Forces the current thread to sleep for msecs milliseconds.
See also sleep() and usleep().
Priority QThread::priority() const
Returns the priority for a running thread. If the thread is not running, this function returns InheritPriority.

This function was introduced in Qt 4.1.
See also Priority, setPriority(), and start().
[slot] void QThread::quit()
Tells the thread's event loop to exit with return code 0 (success). Equivalent to calling QThread::exit(0).
This function does nothing if the thread does not have an event loop.
See also exit() and QEventLoop.
void QThread::requestInterruption()
Request the interruption of the thread. That request is advisory and it is up to code running on the thread to decide if and how it should act upon such request. This function does not stop any event loop running on the thread and does not terminate it in any way.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.2.
See also isInterruptionRequested().
[virtual protected] void QThread::run()
The starting point for the thread. After calling start(), the newly created thread calls this function. The default implementation simply calls exec().
You can reimplement this function to facilitate advanced thread management. Returning from this method will end the execution of the thread.
See also start() and wait().
void QThread::setEventDispatcher(QAbstractEventDispatcher *eventDispatcher)
Sets the event dispatcher for the thread to eventDispatcher. This is only possible as long as there is no event dispatcher installed for the thread yet. That is, before the thread has been started with start() or, in case of the main thread, before QCoreApplication has been instantiated. This method takes ownership of the object.
This function was introduced in Qt 5.0.
See also eventDispatcher().
void QThread::setPriority(Prioritypriority)
This function sets the priority for a running thread. If the thread is not running, this function does nothing and returns immediately. Use start() to start a thread with a specific priority.

The priority argument can be any value in the QThread::Priority enum except for InheritPriorty.
The effect of the priority parameter is dependent on the operating system's scheduling policy. In particular, the priority will be ignored on systems that do not support thread priorities (such as on Linux, see http://linux.die.net/man/2/sched_setscheduler for more details).
This function was introduced in Qt 4.1.
See also Priority, priority(), and start().
void QThread::setStackSize(uintstackSize)
Sets the maximum stack size for the thread to stackSize. If stackSize is greater than zero, the maximum stack size is set to stackSize bytes, otherwise the maximum stack size is automatically determined by the operating system.
Warning: Most operating systems place minimum and maximum limits on thread stack sizes. The thread will fail to start if the stack size is outside these limits.
See also stackSize().
[static protected] void QThread::setTerminationEnabled(boolenabled = true)
Enables or disables termination of the current thread based on the enabled parameter. The thread must have been started by QThread.
When enabled is false, termination is disabled. Future calls to QThread::terminate() will return immediately without effect. Instead, the termination is deferred until termination is enabled.
When enabled is true, termination is enabled. Future calls to QThread::terminate() will terminate the thread normally. If termination has been deferred (i.e. QThread::terminate() was called with termination disabled), this function will terminate the calling thread immediately. Note that this function will not return in this case.
See also terminate().
[static] void QThread::sleep(unsignedlongsecs)
Forces the current thread to sleep for secs seconds.
See also msleep() and usleep().
uint QThread::stackSize() const
Returns the maximum stack size for the thread (if set with setStackSize()); otherwise returns zero.
See also setStackSize().
[slot] void QThread::start(Prioritypriority = InheritPriority)
Begins execution of the thread by calling run(). The operating system will schedule the thread according to the priority parameter. If the thread is already running, this function does nothing.
The effect of the priority parameter is dependent on the operating system's scheduling policy. In particular, the priority will be ignored on systems that do not support thread priorities (such as on Linux, see the sched_setscheduler documentation for more details).
See also run() and terminate().
[signal] void QThread::started()
This signal is emitted from the associated thread when it starts executing, before the run() function is called.
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
See also finished().
[slot] void QThread::terminate()
Terminates the execution of the thread. The thread may or may not be terminated immediately, depending on the operating system's scheduling policies. Use QThread::wait() after terminate(), to be sure.
When the thread is terminated, all threads waiting for the thread to finish will be woken up.
Warning: This function is dangerous and its use is discouraged. The thread can be terminated at any point in its code path. Threads can be terminated while modifying data. There is no chance for the thread to clean up after itself, unlock any held mutexes, etc. In short, use this function only if absolutely necessary.
Termination can be explicitly enabled or disabled by calling QThread::setTerminationEnabled(). Calling this function while termination is disabled results in the termination being deferred, until termination is re-enabled. See the documentation of QThread::setTerminationEnabled() for more information.
See also setTerminationEnabled().
[static] void QThread::usleep(unsignedlongusecs)
Forces the current thread to sleep for usecs microseconds.
See also sleep() and msleep().
bool QThread::wait(unsignedlongtime = ULONG_MAX)
Blocks the thread until either of these conditions is met:
Qt Signal Slot Thread Safe
- The thread associated with this QThread object has finished execution (i.e. when it returns from run()). This function will return true if the thread has finished. It also returns true if the thread has not been started yet.
- time milliseconds has elapsed. If time is ULONG_MAX (the default), then the wait will never timeout (the thread must return from run()). This function will return false if the wait timed out.
This provides similar functionality to the POSIX pthread_join() function.
See also sleep() and terminate().
[static] void QThread::yieldCurrentThread()
Qt Event Vs Signal
Yields execution of the current thread to another runnable thread, if any. Note that the operating system decides to which thread to switch.
Qt Signal Slot Main Thread
© 2019 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.